Building software used to require hiring developers, learning to code, or paying thousands of dollars to outsource development. Not anymore.
Emergent AI represents a fundamental shift in how applications get built, one where natural language replaces programming syntax and multi-agent systems handle everything from design to deployment.
If you’ve heard about “vibe coding” or wondered how entrepreneurs are launching full-scale applications over a weekend, Emergent AI sits at the center of that revolution. This comprehensive guide breaks down what Emergent AI is, how it works, who uses it, and why it matters in 2026.
Understanding Emergent AI: The Basics
Emergent AI is a full-stack, AI-powered application development platform that transforms natural language descriptions into production-ready web and mobile applications.
Unlike traditional coding environments or simple website builders, Emergent uses a sophisticated multi-agent architecture to autonomously design, code, test, debug, and deploy complete software systems.
Think of it as having an entire development team working for you, except that team consists of specialized AI agents that collaborate like human developers would.
You describe what you want to build, and Emergent handles the technical implementation across frontend interfaces, backend logic, databases, API integrations, and cloud hosting.
The platform eliminates the traditional barriers that have kept software development exclusive to technical professionals. No coding knowledge required. No infrastructure to manage. No deployment pipelines to configure. Just conversational interaction that produces functional applications.
The “Vibe Coding” Revolution
Emergent AI exemplifies what the tech industry now calls “vibe coding”—a term coined by OpenAI co-founder Andrej Karpathy in early 2025.
Vibe coding describes the practice of building software by communicating the “vibe” or intent of what you want, rather than writing specific code instructions.
Instead of telling a computer exactly how to execute every function, you describe what you want the application to do and let AI systems figure out the implementation. This represents a paradigm shift from explicit programming to intent-based development.
The term captures how modern AI development works: you express your vision, the AI interprets your goals, generates working code, and iterates based on your feedback. It’s collaborative, conversational, and remarkably fast.
How Emergent AI Works: Multi-Agent Architecture
What separates Emergent AI from simpler AI coding assistants is its agentic architecture. Rather than relying on a single AI model to handle everything, Emergent deploys multiple specialized agents that work together like a professional development team.
The Agent System
Each agent in Emergent’s system has specific responsibilities:
Builder Agent: Takes your natural language description and translates it into technical architecture. This agent decides on the appropriate frameworks, data models, component structures, and integration patterns needed to bring your application to life.
Quality Agent: Reviews generated code for bugs, security vulnerabilities, performance issues, and adherence to best practices. This autonomous testing layer catches problems before they reach production.
Deploy Agent: Handles the complex process of taking your application from development environment to live hosting, managing servers, security configurations, and scalability infrastructure.
Optimizer Agent: Monitors application performance after launch, identifying bottlenecks and suggesting improvements to keep your application running smoothly as it scales.
This division of labor mirrors how actual software companies operate, with different specialists handling different aspects of development. The agents communicate with each other, passing work back and forth to refine the final product.
The Development Process
When you start a new project in Emergent, the workflow unfolds in stages:
- Intent Capture: You describe your application idea in plain English. This could be as simple as “a task manager for remote teams” or as detailed as outlining specific features, user flows, and integrations.
- Planning Phase: The Builder Agent analyzes your requirements and creates a technical plan, determining the appropriate technology stack, database schema, API structure, and component hierarchy.
- Code Generation: Agents generate actual source code across multiple files, creating frontend components, backend services, database models, and integration logic that work together as a cohesive system.
- Testing & Refinement: The Quality Agent automatically tests the generated code, identifying issues and coordinating with other agents to fix problems before you even see them.
- Deployment: With a single action, the Deploy Agent publishes your application to secure cloud infrastructure, handling domain configuration, SSL certificates, and scaling parameters.
- Iteration: You can refine any aspect of your application through continued conversation. Request design changes, add features, modify workflows, or adjust logic—the agents understand context and make appropriate updates.
This isn’t just rapid prototyping. Emergent generates production-grade applications designed to serve real users at scale.
What Makes Emergent AI Different?
The market for AI development tools exploded in 2025, with dozens of platforms claiming to simplify software creation. What distinguishes Emergent from alternatives?
True Full-Stack Development
Many AI coding tools excel at generating user interfaces but struggle with backend complexity. Emergent handles the complete software stack: frontend frameworks, backend APIs, database architecture, authentication systems, payment integrations, and cloud hosting.
You’re not getting pretty mockups that require a developer to wire up later. You’re getting functional applications with working databases, secure user management, and deployed endpoints ready for traffic.
Code Ownership and Portability
A critical advantage of Emergent is that you maintain complete ownership of your application’s source code. The platform provides direct access through Visual Studio Code integration and GitHub export functionality.
This means you’re never locked into Emergent’s ecosystem. If your needs evolve beyond the platform’s capabilities, or if you want to self-host on your own infrastructure, you can export your entire codebase and take it anywhere—to AWS, Vercel, DigitalOcean, or your own servers.
Compare this to traditional no-code platforms where your application exists only within their proprietary system, making it impossible to migrate or customize beyond their constraints.
Beyond Prototypes: Production-Ready Applications
The most significant distinction is architectural depth. Emergent isn’t designed for throwaway prototypes or simple demos. It’s built for creating real businesses, internal enterprise tools, and scalable SaaS products.
The generated code follows industry best practices. Security is baked in with proper authentication flows, encrypted data storage, and secure API integrations. The infrastructure scales automatically as your user base grows. Error handling, loading states, and edge cases are considered during generation.
Companies use Emergent to ship customer-facing products, not just to experiment with ideas.
Advanced Integration Capabilities
Modern applications rarely exist in isolation. They need to connect with payment processors, send emails, integrate with CRM systems, communicate with external APIs, and pull data from various sources.
Emergent’s agents understand how to implement these integrations automatically. Describe the need for Stripe payment processing, and the system generates the appropriate checkout flows, webhook handlers, and transaction management logic. Request Slack notifications, and it builds the integration with proper authentication and error handling.
This extends to AI capabilities themselves. Emergent can integrate advanced machine learning models directly into your applications, enabling features like image generation, natural language processing, voice interfaces, and predictive analytics without requiring ML expertise.
Who Uses Emergent AI?
The platform serves diverse user groups, each leveraging its capabilities in different ways.
Non-Technical Founders and Entrepreneurs
The most obvious beneficiaries are people with strong product visions but no coding background. In 2026, you no longer need a technical co-founder or $50,000 to hire developers just to validate an idea.
Entrepreneurs use Emergent to build minimum viable products (MVPs) in days rather than months, test market fit with real users, iterate based on feedback, and scale products that gain traction—all without writing a single line of code.
This dramatically lowers the barrier to entry for starting software businesses. The playing field has leveled, giving more people the opportunity to turn their ideas into reality.
Indie Developers and Makers
Experienced developers use Emergent to accelerate their workflow, particularly for the repetitive aspects of software development. Instead of spending hours scaffolding boilerplate code, setting up authentication systems, or wiring standard CRUD operations, they let Emergent handle these tasks automatically.
This allows developers to focus their time and skills on the unique, innovative aspects of their projects—the custom algorithms, specialized features, or creative implementations that differentiate their applications.
The speed advantage is substantial. What might take weeks to build manually can be generated and deployed in hours, dramatically increasing how many projects a solo developer can manage simultaneously.
Enterprise Teams and Agencies
Businesses leverage Emergent for internal tool development, creating custom dashboards, workflow automation systems, data visualization tools, and integration platforms without diverting engineering resources from core products.
IT agencies and consultancies use Emergent to deliver client projects faster, reducing project timelines from months to weeks and improving profitability on fixed-price contracts.
The platform’s security features, including role-based access controls, encrypted storage, audit logs, and compliance-ready infrastructure, make it suitable for enterprise environments where data protection and governance matter.
Product Managers and Operations Teams
Even within technical organizations, non-engineering team members use Emergent to prototype features, create internal utilities, and build proof-of-concept applications that demonstrate ideas before involving the development team.
This enables faster experimentation and validation cycles. Product managers can show working prototypes to stakeholders rather than static mockups, leading to better feedback and more informed decision-making.
Key Features That Matter
Understanding Emergent’s feature set helps clarify its capabilities and limitations.
Natural Language Interface
The foundation of the platform is its conversational development experience. You interact with Emergent through natural dialogue, describing features, requesting changes, and refining implementations just as you would explain your vision to a developer.
The system understands context from previous messages, remembers your project’s structure, and interprets ambiguous requests intelligently. This creates a development experience that feels surprisingly human.
Real-Time Preview and Testing
As agents generate code, you see your application taking shape in real-time. Emergent provides live preview environments where you can interact with your application, test functionality, and identify issues before deployment.
This immediate feedback loop dramatically accelerates the iteration process. Spot something you want to change? Describe the adjustment, and watch the application update within seconds.
Automatic Version Control
The platform maintains a complete history of your application’s evolution. Every change creates a versioned snapshot, allowing you to roll back to any previous state if something goes wrong.
This safety net encourages experimentation. Try bold changes knowing you can always revert if the results don’t meet expectations.
Secure Cloud Hosting
Deployment infrastructure is managed automatically. Your applications run in isolated, monitored environments designed for security and reliability. SSL certificates, scaling resources, backup systems, and monitoring dashboards are configured without manual intervention.
For users without DevOps expertise, this removes one of the most intimidating aspects of launching software products.
Collaboration Features
Teams can work together in shared environments. Designers, product managers, developers, and stakeholders can all contribute feedback and suggest changes within the same project workspace.
This collaborative approach bridges the communication gap that often exists between technical and non-technical team members.
Mobile Application Development
Emergent isn’t limited to web applications. The platform generates real iOS and Android mobile apps from the same natural language descriptions, handling platform-specific requirements and ensuring consistent functionality across devices.
This cross-platform capability is particularly valuable for startups that need to serve users on multiple devices without managing separate codebases.
Real-World Use Cases
Understanding how people actually use Emergent clarifies its practical value.
Rapid MVP Development for Startups
A fintech founder needs to validate whether users will pay for a budgeting tool before investing in a full development team.
Using Emergent, they build a functional application in a weekend, complete with user authentication, bank account integration through Plaid, transaction categorization, spending analytics, and payment processing.
They launch to a small group of early adopters, gather feedback, and iterate on features based on real usage data. When the concept proves viable, they either continue building on Emergent or export the codebase to bring development in-house.
Custom Internal Tools for Enterprises
A logistics company needs a custom tracking dashboard that pulls data from their legacy ERP system, displays real-time shipment status, and sends automated alerts to operations teams. Their engineering department is too busy with core product work to build this tool.
An operations manager uses Emergent to create the dashboard, integrating with the existing system’s API, building the visualization interface, and setting up notification logic, all without pulling developers away from priority projects.
Agency Client Deliverables
A digital agency typically takes 8-12 weeks to deliver a custom web application to clients. By using Emergent for initial development, they reduce that timeline to 2-3 weeks, allocating more time to design refinement, content strategy, and client consultation rather than writing boilerplate code.
Their clients receive the same quality product in a fraction of the time, while the agency improves profitability through increased throughput.
E-Commerce and Marketplace Platforms
An entrepreneur wants to launch a niche marketplace connecting local artisans with customers. Building a marketplace traditionally requires complex features: user profiles for buyers and sellers, product listings, search and filtering, shopping carts, payment processing, order management, review systems, and notification workflows.
Emergent generates all these components from a structured description, producing a fully functional marketplace ready for beta testing within days.
AI-Powered Applications
Developers building AI-native products leverage Emergent’s integration capabilities to quickly scaffold applications that use machine learning models. Someone creating an AI writing assistant focuses their efforts on the AI logic and user experience while letting Emergent handle the surrounding infrastructure: user management, subscription billing, document storage, and deployment.
The Broader Context: Agentic AI and the Future of Development
Emergent AI sits at the intersection of several major technology trends reshaping software development in 2026.
The Rise of Agentic Systems
The tech industry is moving beyond simple AI assistants toward autonomous agent systems. Rather than tools that help humans complete tasks, we’re seeing AI systems that can complete tasks independently—planning approaches, executing work, evaluating results, and iterating until goals are achieved.
Industry research indicates that 25% of companies using generative AI implemented agentic AI pilots in 2025, with expectations to double by 2027. This represents a fundamental shift in how organizations think about AI capabilities.
Emergent exemplifies this trend. Its agents don’t just suggest code, they write, test, deploy, and monitor complete applications with minimal human oversight.
Developer Productivity Amplification
GitLab research shows that 78% of development teams have integrated AI-assisted coding tools into their workflows. The transformation isn’t about replacing developers but amplifying their capabilities.
Experienced engineers who embrace these tools ship products faster, handle larger project portfolios, and spend more time on creative problem-solving rather than routine implementation. The same dynamics apply to non-technical builders who can now create software that would have been impossible for them before.
Democratization of Software Creation
Perhaps the most significant impact is accessibility. For decades, software development required extensive technical education, expensive bootcamps, or years of self-taught practice. Emergent and platforms like it are lowering these barriers dramatically.
This democratization means more diverse perspectives building software, more problems being solved through technology, and more economic opportunity for people without traditional tech backgrounds. A restaurant owner can build their own reservation system. A teacher can create educational tools for their classroom. A nonprofit can develop donor management software without burning their limited budget on developers.
The “Day Two” Problem
While many AI development tools focus on the “Day One” problem—how quickly can you generate an initial application?—the more important question is “Day Two”: how do you maintain, debug, scale, and iterate on that software over time?
Emergent addresses this through its ongoing agent support. The Quality Agent continues monitoring for issues. The Optimizer Agent identifies performance improvements. The system maintains clean, readable code that can be understood and modified as requirements evolve.
This distinguishes platforms built for real products from those designed for quick prototypes and demos.
Current Limitations and Considerations
Understanding what Emergent does well requires acknowledging its limitations.
Learning Curve for Complex Customization
While basic applications are straightforward to create, pushing Emergent to build highly complex, custom functionality requires learning how to communicate effectively with the agent system. Describing intricate business logic, unusual data relationships, or sophisticated UI interactions takes practice.
Users coming from development backgrounds often adapt faster because they understand the underlying concepts they’re trying to communicate, even if they’re not writing the code themselves.
Best for Certain Application Types
Emergent excels at standard web and mobile applications: SaaS products, marketplaces, dashboards, internal tools, content platforms, and workflow systems. These represent the vast majority of business software needs.
It’s less suited for applications requiring cutting-edge performance optimization, complex 3D graphics, real-time gaming engines, or highly specialized scientific computing. For those specialized needs, traditional development or specialized tools remain more appropriate.
Iteration for Polish
The initial generation from Emergent creates functional applications quickly, but achieving the exact design aesthetic, specific user experience details, and subtle interaction patterns you envision typically requires iterative refinement.
Users should expect to engage in a back-and-forth process, testing the application, identifying areas for improvement, and requesting adjustments. This is still dramatically faster than traditional development but isn’t instantaneous perfection.
Cost Considerations
While Emergent offers free tiers for exploration, maintaining deployed applications requires paid plans. The hosting, compute resources, and ongoing agent access all carry costs.
For serious products serving real users, these costs are reasonable and typically far lower than hiring developers or using traditional infrastructure. But casual users building hobby projects should understand there’s a monthly expense for keeping applications live.
Getting Started with Emergent AI
For those ready to explore the platform, here’s what to expect.
Account Creation and Onboarding
Access to Emergent begins at app.emergent.sh, where new users can sign up and start building immediately. The interface features a dark-themed design with a prominent text input asking: “What will you build today?”
The platform provides quick-start suggestions, task managers, landing pages, and productivity tools that demonstrate the range of applications you can create. These serve as helpful starting points for understanding how to describe projects effectively.
Your First Build
Starting simple helps build familiarity with how the agent system interprets requests. Describe a straightforward application: “a simple blog where I can write and publish articles” or “a contact form that sends submissions to my email.”
Watch how Emergent structures the project, generates code, and creates a working application. Interact with the preview to see functionality in action.
Once comfortable with basic builds, gradually increase complexity. Add user authentication, integrate with external services, implement payment processing, or create mobile versions.
Documentation and Resources
Emergent provides documentation covering common use cases, integration guides, and best practices for effective agent communication. The learning resources help users understand how to describe complex requirements clearly.
The community around vibe coding platforms has also generated extensive tutorials, templates, and examples that can accelerate your learning curve.
Export and Scaling Options
As your application matures, you can export the source code to GitHub or access it directly through VS Code integration. This gives you the option to continue developing outside the platform, migrate to a different hosting, or bring in developers for specialized customization.
The code Emergent generates follows modern best practices and uses popular frameworks, making it approachable for developers who might join your project later.
Comparing Emergent to Alternatives
The AI application development space includes numerous platforms, each with different strengths.
Replit Agent focuses on the complete development experience with integrated hosting and collaboration features, making it particularly popular for educational contexts and team projects.
Cursor appeals to experienced developers who want AI assistance within a familiar IDE environment, offering powerful code editing capabilities with agent support.
Lovable emphasizes visual design and aesthetics, generating beautiful user interfaces with less focus on complex backend logic.
Bolt.new provides fast generation in browser-based environments, ideal for quick prototyping and experimentation.
Emergent distinguishes itself through its full-stack depth, production-ready output, and multi-agent orchestration. While other tools excel in specific niches—UI beauty, developer experience, rapid prototyping, Emergent aims for comprehensive application development that results in genuinely deployable products.
The Business Model and Pricing
Emergent operates on a tiered pricing structure that reflects the resources required to maintain and host applications.
Free tiers allow exploration and learning, giving users the ability to build and test applications without financial commitment. These tiers typically have limitations on deployed applications, usage quotas, or advanced features.
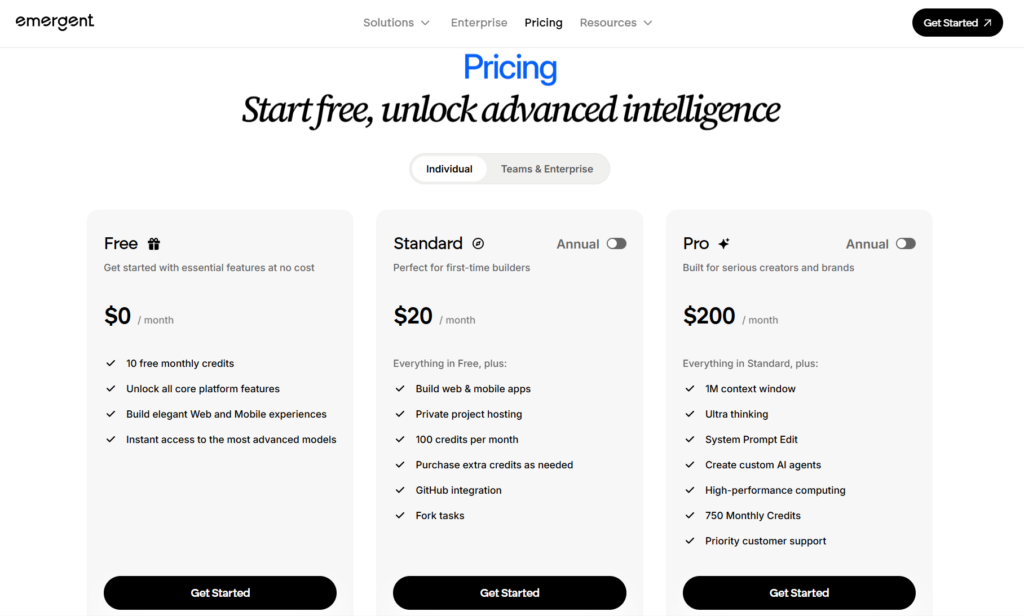
Paid plans unlock full capabilities, including unlimited applications, premium hosting resources, advanced integrations, team collaboration features, and priority agent access. Pricing generally starts around $25-$30 per month for individual developers, with higher tiers for team and enterprise use.
For businesses comparing costs, this remains dramatically more affordable than hiring development talent. A single month of Emergent subscription costs less than a single hour of developer time in many markets, yet provides the capability to build multiple applications.
Security, Compliance, and Enterprise Features
Organizations considering Emergent for business-critical applications need to understand security architecture.
Data Protection
Applications run in isolated containers with encrypted storage. User data never commingles between different projects or customers. Industry-standard encryption protects data both at rest and in transit.
Authentication and Access Control
The platform supports enterprise identity systems through SAML, OAuth, and OpenID Connect integration. This allows organizations to use existing identity providers and maintain centralized access management.
Role-based permissions control who can view, edit, or deploy applications within team workspaces, ensuring appropriate oversight for production systems.
Audit and Monitoring
Audit logs track all actions taken within the platform, providing visibility into who made changes and when. This supports compliance requirements and internal governance policies.
Real-time monitoring tracks application health, performance metrics, and usage patterns, alerting teams to issues before they impact users.
Compliance Readiness
The infrastructure is designed to meet common compliance standards relevant to handling customer data, making it suitable for organizations in regulated industries. However, companies with specific compliance requirements should review Emergent’s certifications and documentation to ensure alignment with their needs.
The Future of Emergent AI and Vibe Coding
Looking ahead, several trends will shape how platforms like Emergent evolve.
Enhanced Multimodal Inputs
Future iterations will likely incorporate voice commands, visual design sketches, and other input modalities beyond text. Imagine describing an application verbally while drawing interface layouts on a tablet, with agents synthesizing all inputs into working code.
Expanded Context Windows
Current AI models have limitations on how much conversation history and project context they can actively consider. As models improve, agents will maintain better understanding of large, complex codebases, enabling them to work on enterprise-scale applications more effectively.
Autonomous Maintenance and Evolution
The vision for agentic development extends beyond initial creation to ongoing maintenance. Future agents may proactively identify security vulnerabilities, suggest performance optimizations, and even implement upgrades to frameworks and dependencies automatically.
Integration with Physical Systems
As AI capabilities expand into physical domains through robotics and IoT devices, platforms like Emergent may enable creation of applications that control hardware, process sensor data, and coordinate physical automation—bringing vibe coding beyond pure software into the physical world.
Standardized Best Practices
As the vibe coding paradigm matures, industry standards for quality, security, and maintainability will emerge. Platforms will converge on best practices that balance speed with reliability, accessibility with expertise, and innovation with responsibility.
Making the Decision: Is Emergent Right for You?
Consider using Emergent if:
- You have an application idea but lack coding skills or access to developers
- You’re an entrepreneur who needs to validate concepts quickly before major investment
- You’re a developer looking to dramatically accelerate your workflow on standard application types
- Your organization needs custom internal tools but can’t spare engineering resources
- You want to maintain code ownership and portability rather than being locked into a platform
- You need production-ready applications, not just prototypes or demos
Emergent may not be the best choice if:
- You’re building applications with extreme performance requirements or highly specialized needs
- You prefer complete manual control over every implementation detail
- Your project requires cutting-edge 3D graphics, real-time gaming, or scientific computing
- You have no budget for hosting costs and need everything free indefinitely
Conclusion: The Transformation of Software Development
Emergent AI represents more than just a useful tool, it exemplifies a fundamental transformation in how software gets built. The barriers that historically kept development exclusive to technical specialists are crumbling, replaced by conversational interfaces and autonomous agent systems that translate intent into implementation.
This isn’t about replacing developers. Experienced engineers using these tools become more productive, tackling larger projects and focusing their expertise on genuinely novel problems. It’s about expanding the population of builders, enabling more people to create technology solutions for the problems they understand best.
In 2026, we’re witnessing the early stages of a shift as significant as the move from mainframes to personal computers, or from desktop software to cloud services. Applications that once required six-figure budgets and months of development time can now be built in days for the cost of a dinner out.
Emergent AI sits at the forefront of this revolution, demonstrating what becomes possible when sophisticated AI agents collaborate to transform natural language into production software. Whether you’re an entrepreneur with a vision, a developer seeking leverage, or a business leader looking to accelerate digital initiatives, understanding platforms like Emergent isn’t optional, it’s essential for navigating the future of software development.
The question isn’t whether AI will reshape how we build applications. That transformation is already underway. The question is how you’ll participate in it.
Frequently Asked Questions About Emergent AI
Is Emergent AI any good?
Yes, Emergent AI is highly effective for building production-ready web and mobile applications without coding. Users successfully launch full-stack SaaS products, marketplaces, internal tools, and dashboards within days instead of months.
The platform excels at standard business applications but works best when users iterate on initial generations to achieve their exact vision.
Thousands of entrepreneurs and developers use it to ship real products serving actual customers, making it one of the leading AI development platforms in 2026.
What does emergence AI do?
Emergent AI transforms natural language descriptions into complete, functional applications using multi-agent AI systems. It generates frontend interfaces, backend APIs, database structures, and handles deployment to secure cloud hosting, all from conversational input.
The platform writes production-grade code across the entire software stack, tests it automatically, and deploys working applications that users can access immediately. Unlike simple code assistants, Emergent builds complete systems including user authentication, payment processing, external integrations, and mobile apps.
Is emergent AI real?
Yes, Emergent AI is a real, operational platform actively used by thousands of developers, entrepreneurs, and businesses in 2026. The platform is accessible at emergent.sh and provides genuine AI-powered application development capabilities. Users build and deploy actual working software through the service, not just prototypes or mockups. The technology behind it, agentic AI systems and large language models, represents current state-of-the-art capabilities in automated software development, not vaporware or future promises.
What does emergent mean in AI?
In AI, “emergent” refers to capabilities that arise unexpectedly from AI systems without being explicitly programmed, abilities that emerge from complex interactions within the system.
Emergent AI as a platform name reflects how sophisticated applications emerge from simple natural language instructions through multi-agent collaboration.
The term captures how the platform’s agents work together to create complex software systems from conversational input, with the final application emerging from the coordinated efforts of specialized AI agents handling different aspects of development.
Is Emergent AI safe?
Yes, Emergent AI implements enterprise-grade security measures including encrypted data storage, isolated application environments, secure authentication systems, and SSL certificates for all deployed applications. The platform maintains industry-standard security practices with role-based access controls, audit logging, and compliance-ready infrastructure.
However, like any development platform, the security of applications you build also depends on how you configure user permissions, handle sensitive data, and implement your specific security requirements. The underlying infrastructure provides a secure foundation for building safe applications.
What is Emergent AI used for?
Emergent AI is used to build SaaS products, e-commerce platforms, internal business tools, mobile applications, custom dashboards, workflow automation systems, MVP prototypes, marketplace platforms, and data visualization tools.
Entrepreneurs use it to launch startups without technical co-founders, developers use it to accelerate project delivery, enterprises build custom internal tools, and agencies create client applications faster.
The platform handles any standard business application requiring user interfaces, databases, APIs, and cloud hosting—essentially any software that doesn’t require specialized performance optimization or cutting-edge graphics.
Is Emergent AI free?
Emergent AI offers a free tier for exploration and learning, but maintaining deployed production applications requires paid subscription plans. Free accounts have limitations on deployed applications, usage quotas, and advanced features.
Paid plans start around $25-30 per month for individual developers and provide unlimited applications, premium hosting resources, team collaboration, and full platform capabilities.
Enterprise plans with advanced security, compliance features, and dedicated support are available at higher price points. The free tier allows you to test the platform and build applications before committing to paid hosting.