Three years ago, OpenAI released a chatbot that would fundamentally alter how we work, learn, and interact with technology.
Today, ChatGPT isn’t just another tech tool—it’s a global phenomenon reshaping the digital economy at a pace that makes even the most optimistic Silicon Valley projections look conservative.
The numbers tell a story of unprecedented adoption. But beneath the headline-grabbing user counts lies a more nuanced narrative about how artificial intelligence is being woven into the fabric of daily work, the emergence of new productivity paradigms, and the fundamental restructuring of how value gets created in the knowledge economy.
Let’s examine what the data actually reveals about where we are, where we’re heading, and what it means for businesses, professionals, and the broader economy.
The Scale: From Zero to Everywhere in Record Time
800 million weekly active users. That’s where ChatGPT stands as of October 2025 (announced by OpenAI CEO Sam Altman at Dev Day), processing approximately 2.5 billion prompts every 24 hours.
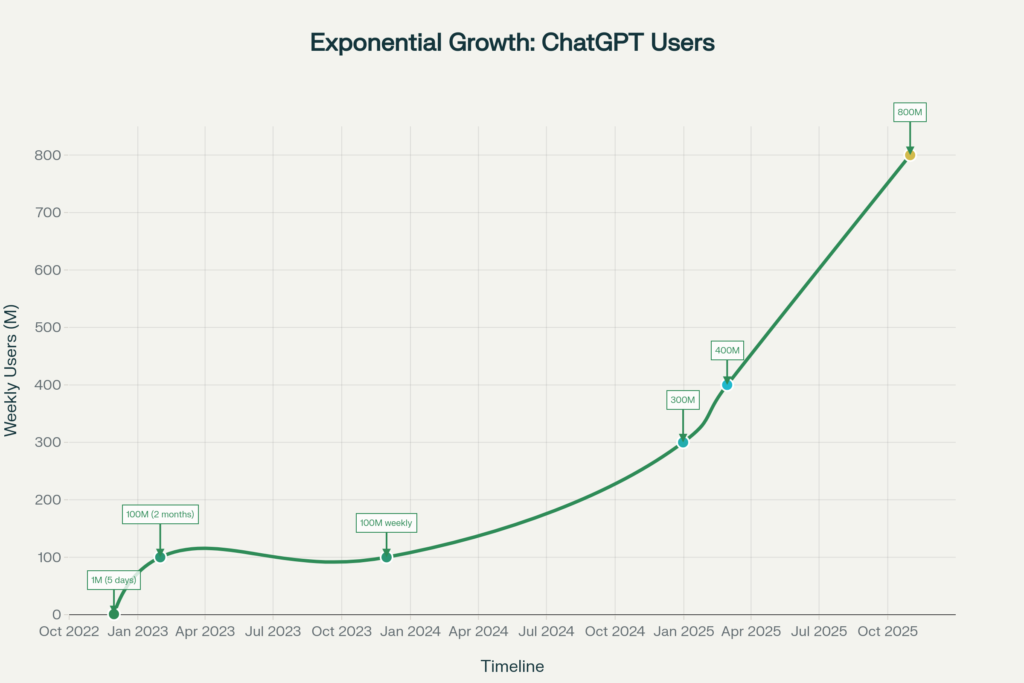
To contextualize this growth: ChatGPT reached 100 million users in just 60 days—faster than any consumer application in history at the time. (Though Meta’s Threads would later claim that crown, its usage has since declined sharply while ChatGPT’s trajectory continues upward.)
The platform now ranks as the 6th most visited website globally, sitting just behind Google, YouTube, Facebook, and a handful of other internet behemoths. That’s not just adoption—that’s integration into daily digital life.
The Growth Trajectory
The numbers reveal exponential, sustained growth:
- November 2023: 100 million weekly active users
- December 2024: 300 million weekly active users
- March 2025: 500 million weekly active users
- August 2025: 700 million weekly active users
- October 2025: 800 million weekly active users
This represents an eight-fold increase in less than two years. Even more telling: the growth rate hasn’t plateaued. OpenAI CEO Sam Altman reported that daily active users quadrupled between 2024 and 2025, suggesting acceleration rather than maturation.
Engagement Beyond Raw Numbers
The real story isn’t just how many people use ChatGPT—it’s how they use it:
- Average session duration: 13-14 minutes (significantly higher than most social media or news platforms)
- Pages per visit: 4.4
- Daily active users: 123 million (as of November 2025)
- Traffic source: 79.77% direct visits (indicating strong brand recall and habitual use)
These metrics point to something more substantial than curiosity-driven experimentation. Users are integrating ChatGPT into workflows, returning regularly, and spending meaningful time engaging with the platform.
The Money: Building a Multi-Billion Dollar Business in 36 Months
Perhaps no statistic better captures ChatGPT’s commercial impact than this: OpenAI hit $10 billion in annual recurring revenue as of June 2025, nearly doubling from $5.5 billion at the end of 2024. More recent reports suggest the figure has climbed to approximately $13 billion by late 2025.
Revenue Breakdown
Approximately 70% of OpenAI’s recurring revenue comes from consumer ChatGPT subscriptions, with the remaining 30% from API services and enterprise products. This consumer-led revenue model is relatively unusual in the enterprise software world, where B2B typically dominates.

The subscription tiers tell their own story:
- ChatGPT Plus ($20/month): 15.5 million paying subscribers as of February 2025, with extraordinary retention rates—89% of subscribers continue after one quarter, and 74% remain after three quarters
- ChatGPT Pro ($200/month): Launched December 2024, already accounting for 5.8% of consumer sales by January 2025, though reportedly unprofitable due to heavy usage by power users
- ChatGPT Enterprise: Driving rapid B2B growth with over 1 million business customers
The Monetization Paradox
Here’s where it gets interesting: despite 800 million users, only approximately 5% are paying subscribers. This creates a fascinating dynamic—OpenAI is generating billions while the vast majority of users access the platform for free.
This isn’t necessarily a weakness. A 5% conversion rate in freemium models is actually above the industry average for AI tools (which sits around 3%). The real question is whether OpenAI can maintain profitability as compute costs scale. Reports suggest the company posted losses of $5 billion in 2024 and projected $8.5 billion in cash burn for 2025, though it’s targeting profitability by 2029 with a long-term revenue goal of $125 billion.
Enterprise Adoption: From Experimentation to Integration
If consumer adoption has been impressive, enterprise penetration has been nothing short of extraordinary. 92% of Fortune 500 companies now have employees using ChatGPT in some capacity—though it’s important to note that formal Enterprise subscription rates are significantly lower. Still, this represents a dramatic shift from 80% within just nine months of ChatGPT’s initial launch.
The Enterprise Numbers
- 1 million+ business customers globally (fastest-growing business platform in history)
- 1.5 million enterprise users as of March 2025 (a 10x increase in one year)
- 7 million ChatGPT for Work seats (40% growth in two months)
- 3 million paying business users across Enterprise, Team, and Edu offerings
Industry Adoption Patterns
The distribution isn’t uniform. High-adoption industries include:
- Technology: 28% of enterprise usage, with 63% of software developers using ChatGPT regularly
- Education/Research: 23% of usage
- Business Services: 11%
- Marketing: 65% of marketing professionals report using the platform
- Journalism: 64% adoption rate
Lower adoption appears in:
- Industrial manufacturing
- Utilities and energy
- Government (though some notable exceptions exist, like the State of Pennsylvania)
The ROI Reality Check
Here’s where the narrative gets complex. While 75% of enterprise leaders report positive ROI from AI investments according to a Wharton study, McKinsey research from March 2025 found that more than 80% of enterprises report no tangible impact on EBIT from generative AI investments.
This paradox—widespread adoption coupled with limited measurable financial impact—suggests we’re in an interesting transitional phase. Companies are integrating AI rapidly, individual users report productivity gains of 30-45% in specific tasks, but the translation to bottom-line results remains elusive for many organizations.
The Geography: A Truly Global Phenomenon
ChatGPT’s reach extends to 195 countries (though it’s banned in 15, including China, Russia, Iran, and North Korea). The geographic distribution reveals interesting patterns:
Top Markets by User Base
- United States: 17-19% of total traffic, approximately 100 million monthly active users
- India: 7-9% of traffic, with notably high daily usage intensity (36% vs. 17% global average)
- Brazil: 5.7% of traffic
- Japan: 3.7% of traffic but with interesting patterns—57.2% monthly usage but only 7.1% daily usage
- Germany: 3.4% (highest in Europe)
Emerging Market Growth
One of the most significant trends: ChatGPT adoption growth rates in the lowest income countries are over 4x those in high-income countries as of May 2025. This democratization of AI access represents a potential shift in global knowledge work dynamics.
Europe shows interesting adoption patterns, with approximately 33% of Europeans having tried ChatGPT at least once. Nordic countries lead within Europe:
- Denmark: 45% penetration
- Sweden: 42%
- Norway: 40%
The Demographics: Who’s Actually Using This?
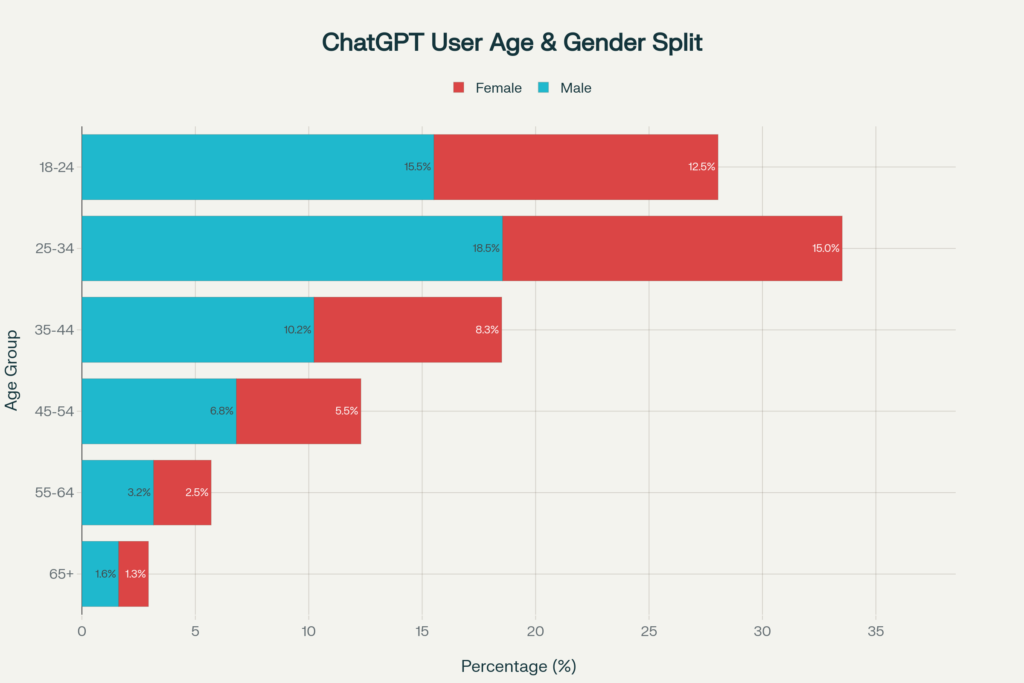
The user base has evolved significantly since ChatGPT’s early-adopter phase.
Age Distribution
- 25-34 age group: 29.93% (largest segment)
- 18-24: 22.55%
- 35-44: 19.89%
- 45-54: 13.61%
- 55-64: 8.52%
- 65+: 5.49%
Younger demographics dominate, but this isn’t surprising for any technology platform. What’s more interesting is the rapid closing of demographic gaps.
The Gender Gap Narrows
In January 2024, approximately 80% of users had typically masculine names. By mid-2025, users with typically feminine names slightly outnumber those with masculine names—a dramatic shift indicating broadening mainstream adoption.
As of August 2025, the gender split is approximately 55.31% male and 44.69% female, approaching population-level distribution.
Education and Professional Patterns
Usage strongly correlates with education and professional role:
- 45% of US adults with postgraduate degrees use ChatGPT daily
- 17% of those with high school education or less use it daily
- 57% adoption in computer-related fields
- 50% in management and business
- 48% in engineering and science
This suggests ChatGPT has become particularly valuable in knowledge-intensive professions—exactly where you’d expect AI to have the highest impact.
Usage Patterns: What People Actually Do With ChatGPT
OpenAI’s Economic Research team, in partnership with Harvard economist David Deming, analyzed 1.5 million conversations to understand actual usage patterns. The findings challenge some assumptions about AI adoption.
The Three Categories of Use
Asking (49% of messages): The largest and fastest-growing category. People primarily use ChatGPT as an advisor—seeking information, guidance, and decision support rather than just task completion.
Doing (40% of usage): Task-oriented interactions including:
- Drafting text (most common work task)
- Planning and organizing
- Coding (still relatively niche)
- Data analysis
Expressing (11% of usage): Personal reflection, exploration, creative play, and experimentation.
Work vs. Personal Use
Approximately 30% of consumer usage is work-related, with 70% being personal. Both categories continue growing, highlighting ChatGPT’s dual role as productivity tool and personal assistant.
Top use cases include:
- Content creation (emails, blog posts, social media)
- Learning and education (tutoring, research, explanations)
- Coding and technical documentation
- Customer support and FAQ generation
- Marketing campaign development
- Personal productivity (scheduling, planning, organizing)
The Economic Value Creation
A Harvard/MIT study at Boston Consulting Group found consultants using GPT-4 completed tasks significantly faster than those without AI assistance—typically 30-40% faster for certain writing and analysis tasks. However, ChatGPT didn’t significantly boost originality, reinforcing its role as “co-pilot” rather than replacement.
Mobile: The Platform That Drives Continued Growth
The mobile app has been crucial to ChatGPT’s expansion:
- 64.27 million downloads in September 2025 (highest monthly figure)
- 43.7% increase in downloads from February to August 2025
- Over 500 million downloads on Google Play alone
- 4.9 rating on both App Store and Google Play
Mobile adoption grew 38% in early 2025, reflecting a shift toward on-the-go AI assistance integrated into daily routines.
Competitive Landscape: Leading, But Not Alone
ChatGPT holds commanding market share but faces growing competition:
- 62.5% of the paid AI tool market (B2C subscriptions)
- 79.76% of the chatbot category
- 80% of all web traffic to generative AI tools (190 million of 240 million average daily visits)
No other paid AI tool commands more than 6% market share. However, new entrants like DeepSeek (which gained 10 million downloads in January 2025), Anthropic’s Claude, Google’s Gemini, and others are intensifying competition.
Interestingly, ChatGPT is projected to hold approximately 1% of the search market in 2025—a small but significant foothold in Google’s domain that represents a shift in how people seek information.
The Challenges Ahead
Despite impressive growth, significant challenges remain:
Financial Sustainability
OpenAI’s path to profitability requires balancing massive infrastructure costs against revenue growth. With commitments exceeding $1 trillion in computing capacity deals over the next decade, the company needs to dramatically increase paying users or find new revenue streams (e-commerce integrations, advertising, enterprise services).
The Productivity Paradox
While individual users report significant productivity gains, many enterprises struggle to demonstrate clear ROI. This gap between bottom-up value and top-down measurement represents a critical challenge for sustained enterprise adoption.
Competition and Commoditization
As AI capabilities become more widespread and multiple strong competitors emerge, ChatGPT must maintain its edge through continuous innovation, superior user experience, and ecosystem lock-in.
Ethical and Regulatory Headwinds
Data privacy concerns, regulatory compliance (especially in Europe with GDPR), content moderation, and questions about AI’s societal impact will continue shaping the product’s evolution.
What This Means for Different Stakeholders
For Business Leaders
The data is unambiguous: AI adoption is no longer optional for competitive advantage. With 92% Fortune 500 penetration, the question isn’t whether to adopt, but how to integrate effectively. Focus on:
- Identifying high-value use cases with clear ROI
- Developing governance frameworks that enable experimentation
- Measuring impact at both individual and organizational levels
- Building AI literacy across teams
For Professionals
ChatGPT is rapidly becoming table stakes for knowledge work. The divide between power users and non-users may translate into productivity and career advantages. Consider:
- Systematic skill development in prompt engineering
- Identifying workflow integration opportunities
- Understanding AI’s limitations to deploy it effectively
- Staying current as capabilities evolve
For Investors
The numbers suggest we’re still in early innings despite massive growth. The 5% paying user conversion rate, continued user growth in emerging markets, and expanding enterprise adoption point to significant runway. However, profitability concerns, intense competition, and massive capital requirements create substantial risk.
For Policymakers
ChatGPT’s global reach—especially rapid adoption in emerging markets—has implications for workforce development, education policy, and economic development. The democratization of AI access could reduce knowledge work disparities or exacerbate digital divides, depending on how adoption and education evolve.
Looking Ahead: Three Trends to Watch
1. From Co-Pilot to Agent
The evolution from passive assistant to autonomous agent capable of executing complex workflows will be crucial. Early signs suggest this shift is underway, with implications for both capability and business model.
2. Vertical Integration
ChatGPT’s expansion into e-commerce (partnerships with Etsy, Shopify, Walmart), the launch of consumer devices, and ambitions to become an “AI cloud” provider represent attempts to capture more of the value chain and reduce dependence on any single revenue stream.
3. The Closing Usage Gap
As adoption broadens across age groups, income levels, and geographies, we’ll see whether the “first-mover” demographics maintain disproportionate usage or if distribution normalizes. The continued narrowing of the gender gap suggests democratization is real, not just aspirational.
The Bottom Line
ChatGPT’s statistics in 2025 tell a story of a technology that has moved beyond hype into genuine integration into daily life and work. With 800 million weekly users, $10-13 billion in annual revenue, and 92% Fortune 500 adoption (at least at the individual employee level)—all achieved in roughly three years—the platform has demonstrated that generative AI isn’t a passing trend but a fundamental shift in how humans interact with information and accomplish knowledge work.
The real question isn’t whether AI will transform work and productivity—that transformation is already underway. The questions that remain are about distribution, sustainability, and whether the productivity gains at the individual level will translate to broader economic value creation or simply represent a new baseline expectation for knowledge work.
For now, the data points in one direction: ChatGPT has moved from exponential curiosity to exponential adoption, and we’re still in the early chapters of this story.
Statistics compiled from OpenAI official reports, industry research from McKinsey, BCG, Wharton School, Reuters Institute, and data analytics from SimilarWeb, Statista, and other authoritative sources. Data current as of November 2025.